Chicago CasiNO!?
Proposal includes casinos for Chicago, Rockford, Danville, Lake County,
South Suburbs of Chicago, Williamson County, plus video slot machines galore.
On February 28th, the Illinois Senate passed SB 7 – a massive gambling bill – by a vote of 31-26. Yet for lawmakers with an insatiable hunger for revenue at the expense of well-documented social costs, it wasn’t enough.
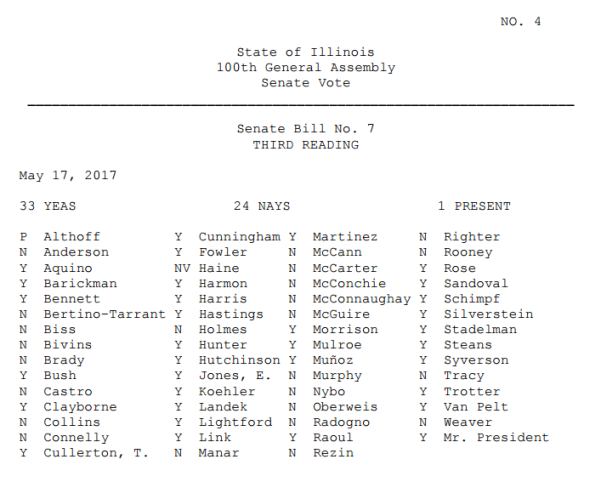
Yesterday, the Illinois Senate passed an amended version of SB 7 to exploit even more citizens, by a vote of 33-24 with 1 voting present. (See roll call chart below.)
This oppressive and myopic legislation is sponsored by Illinois Senators Terry Link (D-Gurnee), Dave Syverson (R-Rockford), Mattie Hunter (D-Chicago) and Donne Trotter (D-Chicago). The passage of this bill demonstrates that our state lawmakers are not serious about solving the fiscal problems of the state — specifically the wasteful spending and bloat that is Illinois government. Instead, a majority of politicians in the Illinois Senate gave their stamp of approval to an unstable and unfair source of “revenue,” while ignoring the many social costs that come with a vice like gambling.
According to Illinois Churches in Action, this legislation will give special perks to the gambling industry while soaking hard working families:
SB 7 includes a massive casino for Chicago, slots machines at Chicago Airports, additional land-based casinos for Rockford, Danville, Lake County, South Suburbs of Chicago, Williamson County Winery, and at 4 racetracks.
SB 7 allows progressive jackpots at casinos and video gambling establishments and expands video gambling by doubling the maximum bet and more than doubling the jackpot.
The bill lowers taxes on slot machines and table games and gives tax breaks to racetracks and casinos. SB 7 will not solve the budget problem, but it will increase addiction and problem gambling.
Take ACTION: Click HERE to send your state representative an email or a fax to tell them “NO MORE GAMBLING — PERIOD.” Don’t delay in speaking out. With only 2 weeks left before state lawmakers adjourn for the summer, this gambling bill may move fast.
Background
In addition to the 10 casinos Illinois currently has, residents face the prospect of an additional 6 casinos (for a total of 16), making Illinois a top contender for the most anti-family and predatory gambling state in the nation. If we consider all the video slot machines currently in the state, plus all the Lottery fleecing “games,” we are well underway to securing the title of being the top “swindle state” in America.
Think about the devastation a casino would bring to the poorest families in Chicago. Impoverished working poor would be encouraged by this foolish policy to seek out the elusive “pot of gold” — and the “key” to happiness by gambling away their meager resources. To make matters worse, they would have easy access to a Chicago casino via public transportation.
Moreover, the National Gambling Impact Study Commission estimated that approximately 15 million U.S. citizens have a gambling problem and/or are pathological gambling addicts. Their research also shows that addiction rates double within 50 miles of a casino. Think of all the people within a 50-mile radius of 15 casinos and how many new gambling addicts the state will help produce with this foolish proposal. There is enormous potential for many new gambling addicts in Chicago-land alone. How is this good public policy?
The American Psychiatric Association says that symptoms of pathological gambling include the following: lying about the amount of time or money spent gambling, needing to borrow money to get by due to gambling losses, gambling larger amounts of money to try to win back previous losses, and committing crimes to obtain money to gamble.
Researchers believe that crimes committed by compulsive gamblers are often under-reported. Some of these crimes include writing bad checks, check forgery, fraud, and embezzlement.
Some gamblers turn to street crime. The National Institute of Justice reported that 30 percent of pathological gamblers who were arrested in Las Vegas and Des Moines admitted that they had committed a robbery within the past year. About 13 percent of them admitted they had assaulted someone to get money.
Although some people win at the casinos, winning consistently is rare. And those people who believe they will win their money back after a losing streak are deluding themselves. The truth is one in five people addicted to gambling will file for bankruptcy. Casinos would not be able to stay in business if people won more than they lost.
Studies also show that both divorce and suicide rates are higher for pathological gamblers than non-gamblers. Gamblers Anonymous surveyed approximately 400 members and found that two-thirds had thought of suicide, 77 percent had wanted to die, and 47 percent had a definite plan to kill themselves.
Economics professor, Earl Grinols, says in his book, Gambling in America: Costs and Benefits, the annual cost of one addicted gambler to society is $10,330. Grinols argues that the costs of casino-derived revenues exceed the benefits by a factor of more than 3 to 1.
It is clear, the social costs of gambling far outweigh any perceived benefits.
How did they vote?
For up-to-the minute news, action alerts, coming events and more you can now sign up for IFI Text Alerts!
Stay in the loop with IFI by texting “IFI” to 555888 to be enrolled right away.

